Fibre to Fabric (Part - 3) class 6
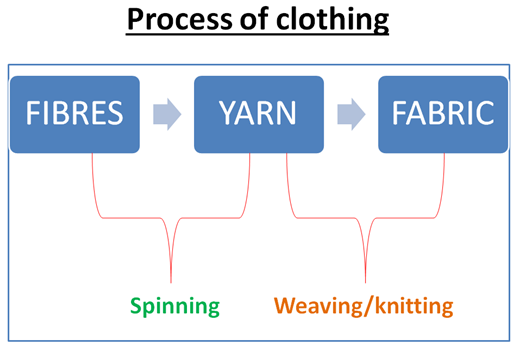
Fibre to Fabric Q.18. What are the two steps involved in the process of making fabrics from fibres? Ans. Fabrics are made from fibres in the following two steps: i) Fibres are first converted to yarn by the process of spinning . ii) Fabric is made from yarn by the process of Weaving or Knitting . Q.19. What is spinning and how is it done? Ans. The process of making yarn from fibres is called spinning . In this process, fibres from a mass of any fibre are drawn out and twisted. This brings the fibres together to form a yarn. Q.20. Name three devices for making yarn from fibres. Ans. Yarn can be made from fibres by using three devices: i) Hand spindle (Takli) ii) Spinning wheel (charkha) iii) Spinning machines Q.21. Which spinning device was popularized by Mahatma Gandhi as a part of Independence movement? Ans. Use of Spinning wheel (charkha) was popularised by Mahatma Gandhi as part of the Ind...



